⛓️ Key Supply Chain Challenges in 2025
What’s driving supply-chain manufacturing risk right now? Follow trends and focus on mitigation strategies!

Primary Supply Chain Challenges in Manufacturing
Manufacturers entered 2025 confronting a supply chain landscape that is both volatile and opportunity-rich. Trade policy shifts, climate-driven disruptions, and a widening talent gap are amplifying traditional cost and service pressures. Yet, digital technologies and landmark industrial policies are unlocking new pathways to resilience.
Statistics and Insights for 2025
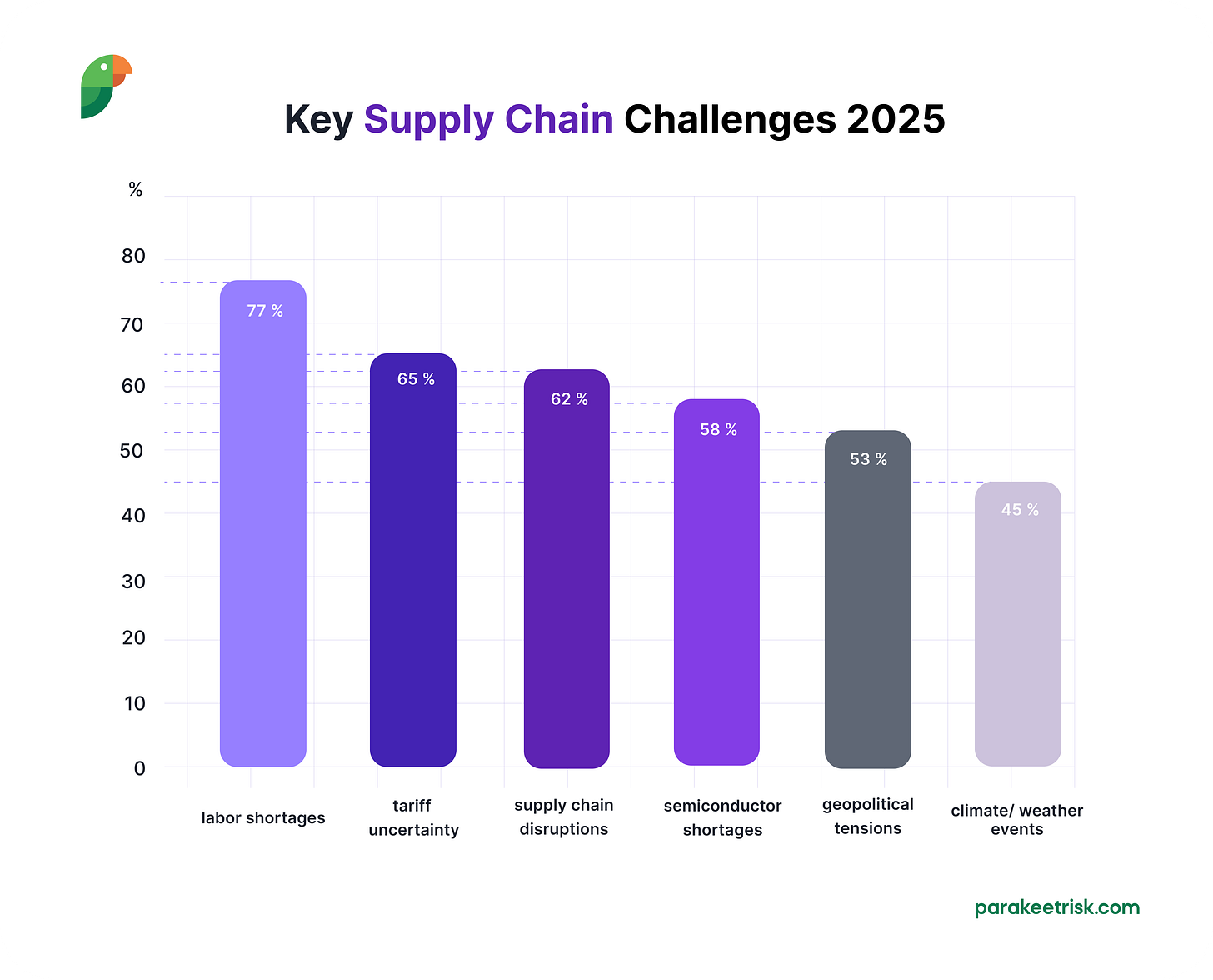
The latest cross-industry polling shows that executives perceive 2025’s supply chain threats as markedly different in scale and nature from the pandemic era. Manufacturers rank labor shortages as the most widespread supply chain challenge for 2025, well ahead of tariffs and semiconductor delays.
Key supply chain challenges facing manufacturers in 2025, showing labor shortages as the primary concern affecting 77% of companies.
1. Chronic Labour Shortages
Seventy-seven percent of manufacturers report that finding and retaining skilled workers is their number one operational constraint. A record share of Baby Boomers is retiring while advanced automation roles remain unfilled.
Implications:
Lower capacity utilisation (U.S. factories averaged 74.1% in Q1-25, three points below the 20-year norm).
Longer lead times for customised or engineer-to-order products.
Escalating wage inflation outpacing pricing power in commodity-like sectors.
2.1 million manufacturing jobs could go unfilled by 2030.
Mitigation Playbook:
👉 Adopt automation solutions, such as co-bot and lights-out cell strategies that redeploy scarce labour from repetitive tasks to higher-value problem solving.
👉 Launch apprenticeship consortia in partnership with community colleges; Germany-style dual training is regaining traction in Ontario and the U.S. Midwest.
👉 Implement skills-based scheduling analytics that pair veteran workers with cross-training opportunities to stem turnover.
2. Geopolitical and Trade Policy Uncertainty
65% of companies cite tariff uncertainty as a major supply chain concern. Tariff implementation represents a significant operational risk, with potential duties on Canadian and Mexican goods threatening energy products, pulp and paper, and automotive parts supply. The complexity of these trade relationships means that supply chain rerouting and supplier diversification efforts create temporary disruptions.
Tariff policies included:
25% duties on foreign vehicles and components (May 2025)
50% tariffs on steel, aluminium, and copper imports.
Implications:
Tariffs imposed on USMCA-compliant goods from Mexico during March 4-6, 2025, created unexpected logistics cost increases that companies were unable to pass through to customers due to the brief implementation period.
Mitigation Playbook:
👉 Tariff volatility has become a core industrial risk. Companies must invest in real-time trade monitoring, scenario planning, and flexible supplier networks.
👉 Read more about tariffs on our blog:
3. Persistent “Grey” Disruptions
62% of companies experience ongoing supply chain disruptions (logistics, port delays, etc.), which keeps inventories thin and leads to volatile lead times.
More than 60% of plants cite generic delays—port congestion, container shortages, rail service unreliability—echoing the logistical aftershocks from 2024’s Red Sea diversions and Panama Canal throughput caps. Enterprises are diversifying beyond single-country ocean routings and developing scenarios around dual sourcing of critical tier-2 materials.
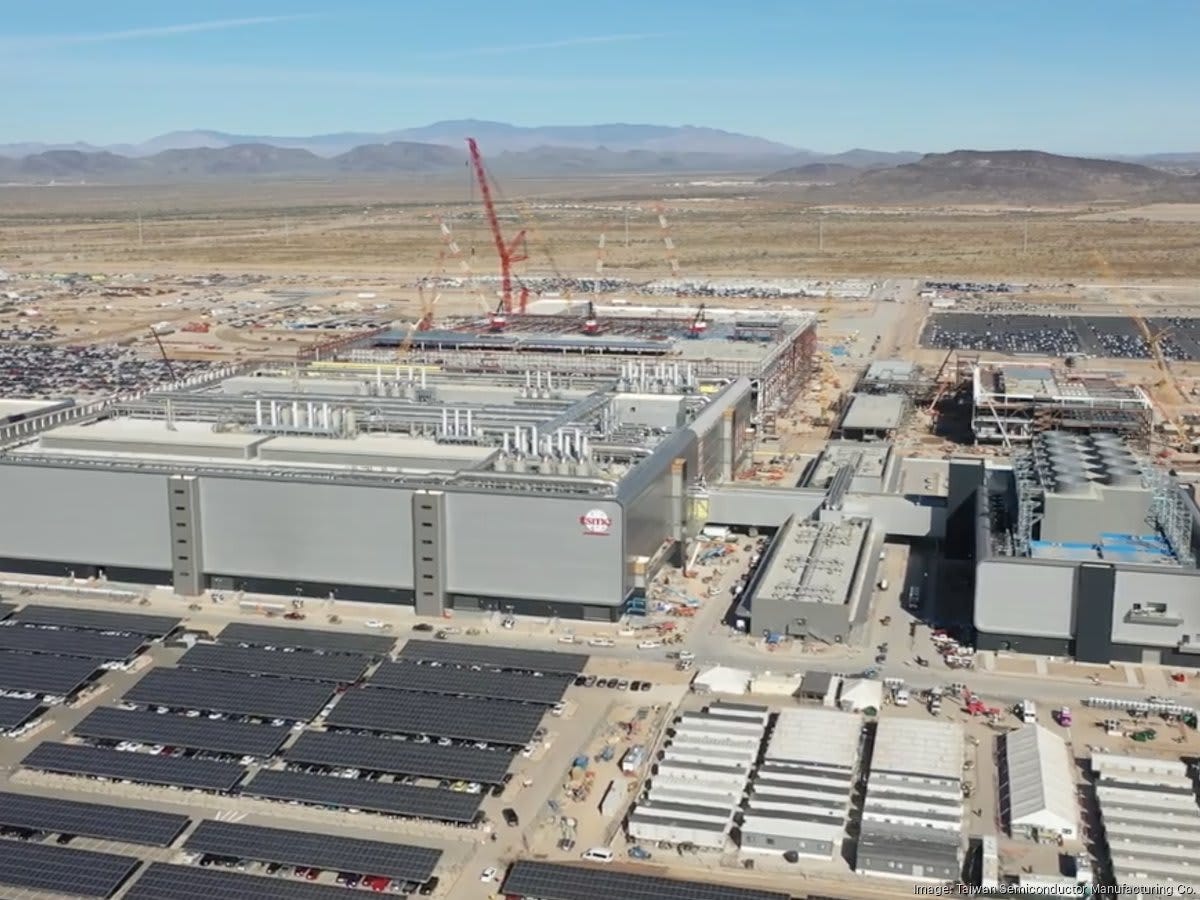
4. Semiconductor Capacity Lag
Despite $52 billion in CHIPS Act incentives, lead times for certain AI and automotive microcontrollers remain above 30 weeks. Labour hurdles—qualified fab technicians and construction electricians—mean many U.S. greenfield fabs will not reach volume production until late 2026.
New chip shortage risks emerging from geopolitical tensions and tariff actions.
TSMC's Arizona semiconductor fabrication facility under construction. Source: bizjournals.
Mitigation Playbook:
👉 Real-Time Monitoring Tools: Deploy AI-driven analytics and IoT solutions to track global supply risks, anticipate disruptions, and optimize procurement decisions in real time.
👉 Blockchain for Traceability: Adopt blockchain technology to enhance traceability of chips and raw materials, and to reduce exposure to counterfeiting or black-market sources.
👉 Accelerate Training Programs: Collaborate with academic institutions and technical schools to fast-track programs for fab technicians, engineers, and electricians, leveraging CHIPS Act-funded STEM initiatives.
5. Extreme Weather as a Structural Risk
45% of companies report weather events causing supply chain disruptions. Floods, droughts, and hurricanes directly hit key facilities.
Floods accounted for about 70% of all weather-related supply chain disruptions in 2024.
The United States experienced a sharp increase in severe flood events, with flood alerts doubling since 2023, particularly impacting transportation, raw material supply, and plant operations.
NOAA projects a 60% chance of an above-average Atlantic hurricane season for 2025, forecasting 13 to 19 named storms, including up to 5 major hurricanes (Category 3 or higher).
Many plants built decades ago are now exposed to drastically increased flood risk, resulting in major hardening and redesign investments.
Mitigation Playbook:
👉 Common mitigation strategies include elevating equipment, upgrading storm barriers, and revising inventory positioning and supplier strategies to account for climate-driven volatility.
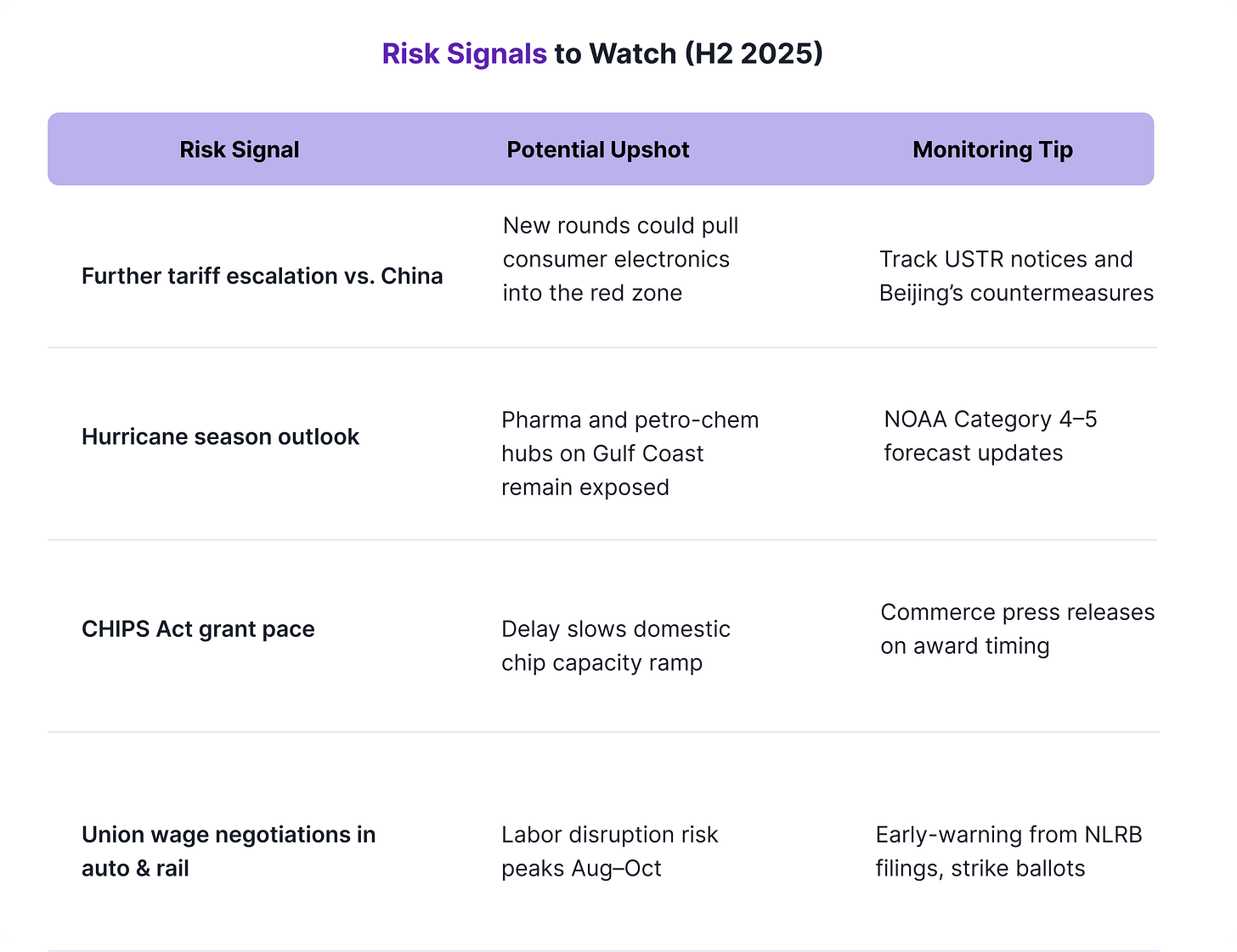
Critical Risk Signals Demand Strategic Vigilance in H2 2025
These risk signals underscore a fundamental shift in the business environment—where traditional operational planning must now incorporate real-time geopolitical, environmental, and social monitoring.
Trade tensions with China represent perhaps the most acute immediate risk, with potential tariff escalations threatening to push consumer electronics manufacturers into unprofitable territory. The stakes couldn't be higher—companies must maintain constant vigilance over U.S. Trade Representative announcements and Beijing's countermeasures to avoid being caught off-guard by sudden policy shifts that could devastate margins overnight.
The Atlantic hurricane season presents another formidable challenge, with pharmaceutical and petrochemical facilities along the Gulf Coast facing elevated exposure to Category 4-5 storms. Given the critical nature of these industries to national supply chains, executives should closely monitor NOAA's severe weather forecasts and implement robust contingency plans to protect both infrastructure and continuity of operations.
Meanwhile, the CHIPS Act implementation continues to face concerning delays that could undermine America's semiconductor independence goals. The sluggish pace of grant distribution threatens to postpone crucial domestic chip capacity expansion, making it essential for industry leaders to track Commerce Department press releases and adjust their technology roadmaps accordingly.
Perhaps most immediately disruptive are the looming labor negotiations in the automotive and rail sectors, where union wage discussions through August and October carry significant strike potential. Companies should establish early-warning systems by monitoring labor board filings and strike ballot developments, as work stoppages in these interconnected industries could trigger cascading supply chain failures.
The most resilient organizations will be those that transform these threats into competitive advantages through superior intelligence gathering and adaptive response capabilities.
👉 Get more insight into the topic of Supply Chain Challenges on the Parakeet Risk blog:
Never miss an update—subscribe to the Process Control Newsletter for more compliance insights, tips, and best practices!